US Carbon Capture Innovations: Q1 2025 Policy & Tech Brief

The landscape of US Carbon Capture Innovations is rapidly evolving, with Q1 2025 marking critical shifts in policy and technology. Recent developments are poised to redefine the nation’s approach to industrial decarbonization and climate change mitigation, urging stakeholders to stay informed on these crucial updates.
Q1 2025 Policy Landscape: New Incentives and Regulatory Frameworks
As of Q1 2025, the United States is seeing a robust push for new policy incentives aimed at accelerating carbon capture, utilization, and storage (CCUS) projects. These frameworks are designed to provide financial stability and regulatory clarity, crucial for attracting investment and scaling up deployment across various industrial sectors. The focus remains on creating an environment that supports both technological innovation and practical implementation.
Federal agencies are actively working to streamline permitting processes, a longstanding bottleneck for CCUS projects. The goal is to reduce lead times for project approvals, allowing for faster construction and operation. This regulatory acceleration is critical for meeting ambitious decarbonization targets set for the coming decades.
Key Legislative Updates Impacting CCUS
Several legislative proposals and enacted laws are shaping the current policy environment. These include amendments to existing tax credits and the introduction of new grant programs specifically targeting carbon capture technologies. These measures aim to make CCUS economically viable for a broader range of industries, from power generation to heavy manufacturing.
- 45Q Tax Credit Enhancements: Recent adjustments to the 45Q tax credit are making CCUS projects more attractive, increasing the credit value for captured carbon and extending the construction commencement window.
- Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act Funding: Significant allocations from this act continue to funnel into CCUS demonstration projects and commercial-scale deployments, providing essential seed money for nascent technologies.
- State-Level Initiatives: Beyond federal efforts, several states are implementing their own incentive programs and regulatory bodies to support CCUS, often tailored to their specific industrial bases and geological storage potential.
Technological Breakthroughs: Advancements in Capture and Storage
The first quarter of 2025 has witnessed a surge in technological advancements within the carbon capture sector. Innovations are emerging across the entire CCUS value chain, from more efficient capture methods at the source to enhanced storage solutions. These breakthroughs are crucial for reducing the cost and energy intensity of CCUS, making it a more viable option for widespread adoption.
Research and development efforts are primarily focused on improving absorbent materials, developing novel membrane technologies, and optimizing direct air capture (DAC) systems. These innovations promise to lower operational costs and increase the capture efficiency of CO2, addressing some of the historical challenges associated with CCUS.
Next-Generation Capture Methods
New methods for capturing carbon dioxide are moving beyond traditional amine-based systems. Scientists and engineers are exploring solid sorbents, metal-organic frameworks (MOFs), and enzymatic approaches that offer higher selectivity and lower energy penalties. These technologies are particularly promising for applications where flue gas streams are dilute or have low CO2 concentrations.
- Solid Sorbent Development: Researchers are developing solid sorbents that can capture CO2 at lower temperatures and regenerate with less energy, leading to significant cost reductions.
- Membrane Technology Evolution: Advanced membrane systems are becoming more robust and selective, offering a compact and energy-efficient solution for CO2 separation, especially in industrial settings.
- Direct Air Capture (DAC) Scale-Up: Significant investments are flowing into DAC technologies, with several pilot projects demonstrating improved capture rates and reduced energy consumption, bringing large-scale deployment closer to reality.
Major Project Developments and Commercial Deployments
Q1 2025 is characterized by a notable uptick in the announcement and progression of major carbon capture projects across the US. These projects span various industries, including cement, steel, power generation, and hydrogen production, showcasing the versatility and growing adoption of CCUS technologies. Many are backed by a combination of private investment and federal funding, signaling strong confidence in their long-term viability.
Several commercial-scale facilities are moving from planning stages to active construction, with some even beginning initial operations. These early deployments are critical for gathering real-world data, optimizing processes, and demonstrating the economic and environmental benefits of CCUS to a broader audience. The lessons learned from these pioneering projects will inform future developments and accelerate the learning curve for the entire industry.
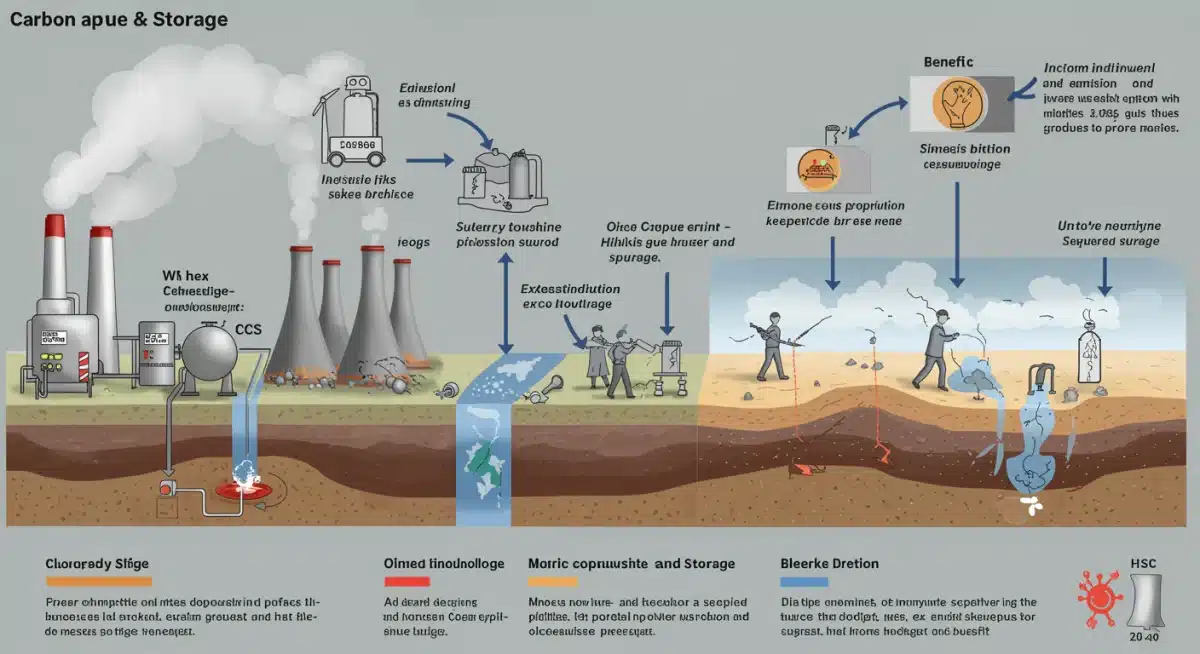
One notable trend is the emergence of regional carbon capture hubs, which aim to collect CO2 from multiple industrial sources and transport it via shared pipeline infrastructure to centralized geological storage sites. This collaborative approach reduces individual project costs and increases efficiency, fostering a more integrated and scalable CCUS ecosystem.
Economic Analysis: Costs, Benefits, and Investment Trends
A critical aspect of US Carbon Capture Innovations in Q1 2025 involves a detailed economic analysis of costs, benefits, and prevailing investment trends. The economic viability of CCUS is improving due to technological advancements and supportive policies, making it an increasingly attractive option for industries facing decarbonization mandates. Project financing models are also evolving, incorporating a mix of public and private capital.
The cost of capturing a ton of CO2 is a key metric, and recent data indicates a downward trend for several technologies. This reduction is attributed to economies of scale, improved process efficiency, and ongoing research and development. Furthermore, the value of captured CO2 in utilization applications, such as enhanced oil recovery or the production of sustainable fuels and chemicals, adds another revenue stream that can offset operational costs.
Investment Landscape and Market Outlook
The investment landscape for CCUS is robust, with venture capital, private equity, and major industrial players pouring funds into innovative startups and large-scale projects. The market outlook remains positive, driven by increasing corporate sustainability commitments and tightening environmental regulations. Investors are recognizing the long-term potential of CCUS as a critical tool for achieving net-zero emissions.
- Private Sector Engagement: Energy companies, chemical manufacturers, and industrial giants are making significant direct investments in CCUS projects and R&D.
- Government Funding Programs: Federal grants and loan guarantees continue to de-risk early-stage projects, attracting private capital into the sector.
- Carbon Markets Influence: The development and expansion of voluntary and compliance carbon markets are creating financial incentives for CO2 reductions, further stimulating CCUS investments.
Environmental Impact and Social Considerations of CCUS
Understanding the environmental impact and addressing social considerations are paramount when navigating US Carbon Capture Innovations. While CCUS offers a powerful solution for reducing greenhouse gas emissions, its deployment must be managed responsibly to ensure ecological integrity and community acceptance. Q1 2025 sees an increased focus on these aspects, with robust environmental assessments and public engagement strategies becoming standard practice.
Environmental concerns primarily revolve around the potential for CO2 leakage from storage sites, the energy footprint of capture processes, and the responsible sourcing of materials for CCUS infrastructure. Rigorous monitoring protocols and advanced geological modeling are being implemented to mitigate leakage risks, ensuring the long-term containment of stored CO2. The industry is also working to minimize the energy demand of capture technologies through ongoing innovation.
Community Engagement and Environmental Justice
Social considerations, particularly related to environmental justice, are gaining prominence. Developers are increasingly engaging with local communities early in the project lifecycle, addressing concerns about safety, land use, and potential impacts on local economies. Transparency and clear communication are vital for building trust and ensuring that the benefits of CCUS are equitably distributed.
- Stakeholder Consultations: Extensive public hearings and community meetings are being held to inform residents and gather feedback on proposed CCUS projects.
- Rigorous Site Selection: Geological storage sites are chosen based on comprehensive assessments to ensure long-term stability and minimize environmental risks.
- Water Usage Optimization: Efforts are underway to reduce the water demands of CCUS processes, especially in water-stressed regions, through technological advancements and efficient operational practices.
International Comparisons and Global Collaboration in CCUS
Q1 2025 highlights the increasing importance of international comparisons and global collaboration in advancing US Carbon Capture Innovations. The United States is actively engaging with other nations that are leaders in CCUS, sharing best practices, technological insights, and policy frameworks. This global exchange is crucial for accelerating the deployment of CCUS worldwide and achieving collective climate goals.
Nations like Norway, Canada, and the UK have long been at the forefront of CCUS development, particularly in offshore storage and industrial applications. Learning from their experiences, both successes and challenges, provides valuable lessons for US projects. Collaborative research initiatives and joint demonstration projects are also fostering innovation and reducing development costs for all participants.
Harmonizing Standards and Cross-Border Projects
Efforts are underway to harmonize international standards for CCUS measurement, reporting, and verification (MRV), which will facilitate cross-border CO2 transport and storage. This standardization is essential for creating a global market for captured carbon and enabling larger-scale projects that span national boundaries. The development of international carbon accounting rules also plays a significant role in this harmonization.
- Bilateral Agreements: The US is forging bilateral agreements with key partners to facilitate technology transfer and joint investment in CCUS projects.
- Multilateral Forums: Active participation in forums like the Clean Energy Ministerial and the Carbon Sequestration Leadership Forum promotes dialogue and cooperation on CCUS policy and technology.
- Shared Research Agendas: International research consortia are tackling common challenges in CCUS, such as improving capture efficiency and ensuring safe, long-term storage, benefiting all participating countries.
| Key Point | Brief Description |
|---|---|
| Policy Incentives | Q1 2025 sees enhanced federal tax credits and streamlined permitting processes driving CCUS project viability. |
| Tech Advancements | Breakthroughs in solid sorbents, membrane tech, and DAC are reducing costs and improving CO2 capture efficiency. |
| Project Deployments | Numerous commercial-scale CCUS projects are progressing, with a focus on regional hubs and diverse industrial applications. |
| Global Collaboration | The US is actively engaging with international partners to share knowledge and harmonize standards for CCUS. |
Frequently Asked Questions About US Carbon Capture Innovations
The primary policy drivers are enhanced 45Q tax credits and significant funding from the Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act. These incentives aim to reduce financial risks for developers and accelerate the deployment of CCUS technologies across various industrial sectors, fostering a more sustainable energy future.
New technologies are improving efficiency through advancements in solid sorbents, advanced membrane systems, and optimized direct air capture (DAC) processes. These innovations are designed to lower the energy consumption and operational costs associated with capturing CO2, making large-scale deployment more economically feasible and environmentally beneficial.
Major project developments in Q1 2025 include commercial-scale CCUS facilities in heavy industries like cement, steel, and power generation. There’s also a growing focus on establishing regional carbon capture hubs, which consolidate CO2 from multiple sources for efficient transport and centralized geological storage, enhancing scalability.
Economic factors driving investment include decreasing capture costs, increasing value from CO2 utilization, and robust government funding. Corporate sustainability goals and expanding carbon markets also play a crucial role, creating financial incentives for industries to adopt CCUS as a viable solution for emissions reduction and long-term climate goals.
The US is addressing these concerns through rigorous environmental impact assessments, stringent monitoring protocols for storage sites, and proactive community engagement. Emphasis is placed on transparency, clear communication with local populations, and ensuring environmental justice principles are upheld during project planning and implementation to foster trust and acceptance.
Looking Ahead: The Future of US Carbon Capture
The rapid pace of developments in US Carbon Capture Innovations during Q1 2025 signals a transformative period for industrial decarbonization. The convergence of supportive policies, groundbreaking technologies, and increasing investment momentum suggests that CCUS is poised to play an even more central role in the nation’s climate strategy. Stakeholders should anticipate continued regulatory evolution, further technological breakthroughs, and an expansion of commercial deployments as the US strives to meet its net-zero emission targets. The focus will likely shift towards optimizing existing projects and fostering broader public acceptance, ensuring a sustainable and equitable energy transition.